机器学习
Python与Pytorch基础
张量基础 tensor
- PyTorch中的所有操作都基于张量(一种包含多种处理方法的容器对象)。
- 张量可以简单的看作是一个多维度的列表(List)。
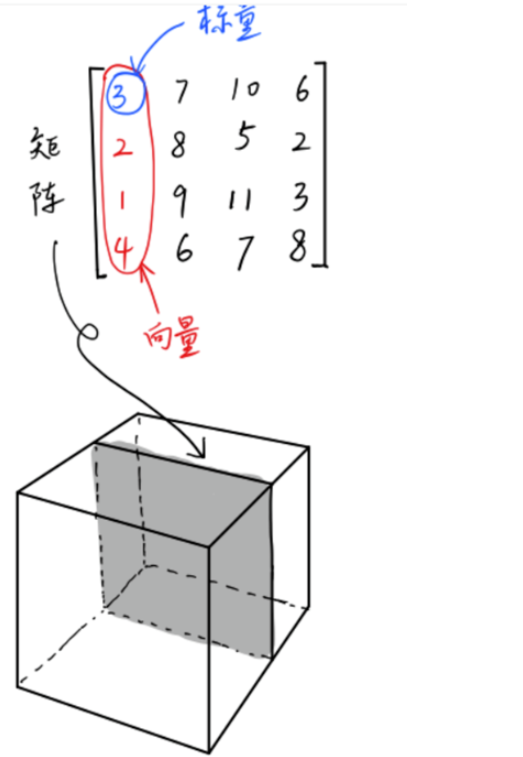
其实,也可以将标量和向量视为张量:
标量是零维的张量 => 3,2,1, 4 只有大小,没有方向
向量是一维的张量 => [3,2,1, 4], [7, 8, 9, 6] 有大小和方向的一串数字
矩阵是二维的张量 => 几个向量合并而成
PyTorch是非完备的编程语言库,而是用于加速神经网络训练的框架,因此并没有string这种类型。
案例练习
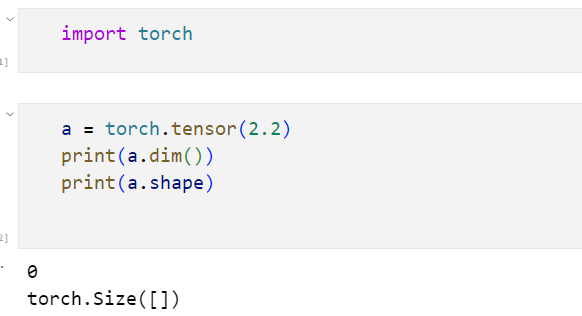
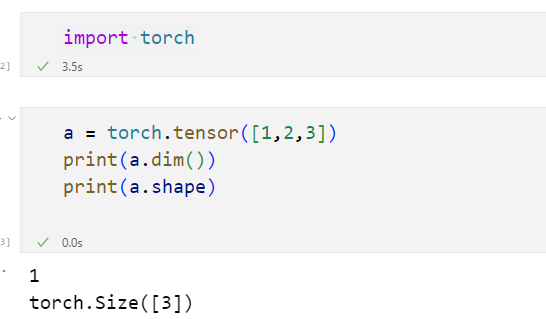
PyTorch的标量和张量
 |  |
|---|
python
a = torch.tensor([2.2])
b = torch.tensor([1.1,2.3])
c = torch.tensor([[1.1,1.2,1.3],
[2.1,2.2,2.3]
])
print(a.dim(),b.dim(),c.dim())
print(a.shape,b.shape,c.shape)
'''
1 1 2
torch.Size([1]) torch.Size([2]) torch.Size([2, 3])
'''参数解释:
dim 计算维度
shape 读取矩阵的长度,比如shape[0]就是读取矩阵第一维度的长度
创建随机的张量
python
a = torch.rand(2,3)
b = torch.randn(2,3)
# torch.randn(2,3) 初始化一个符合正态分布的张量 创建全0或者全1的张量
print(a)
print(b)
'''
tensor([[0.7770, 0.6402, 0.5048],
[0.9622, 0.8443, 0.5780]])
tensor([[-0.6340, -0.9222, 0.1695],
[-1.5033, 0.9106, -1.3766]])
'''创建全0或者全1的张量
python
a = torch.zeros(2,3)
b = torch.ones(2,3)
print(a)
print(b)
a.shape
'''
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
torch.Size([2, 3])
'''查看张量的数据类型
python
a.dtype
'''
torch.float32
'''在创建张量的时候,指定类型
python
a = torch.zeros(2,3,dtype=torch.float16)
print(a)
print(a.dtype)
'''
a = torch.zeros(2,3,dtype=torch.float16)
print(a)
print(a.dtype)
'''创建指定值的张量,torch.tensor(list)
python
x = torch.tensor([5.5,3])
print(x)
'''
tensor([5.5000, 3.0000])
'''张量的运算
python
x = torch.rand(2, 2)
y = torch.rand(2, 2)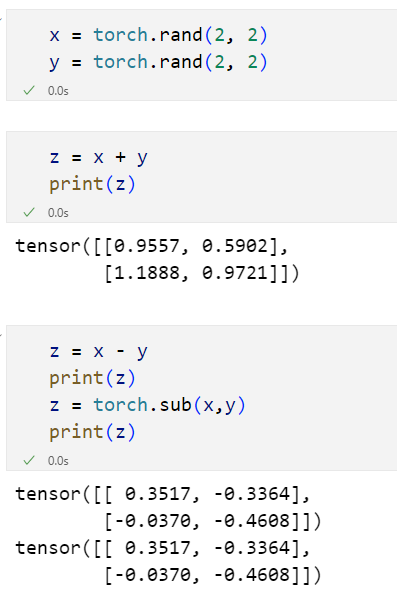 | 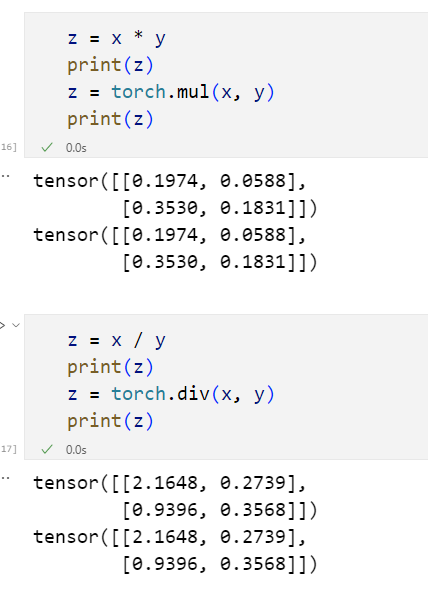 |
|---|
张量的切片
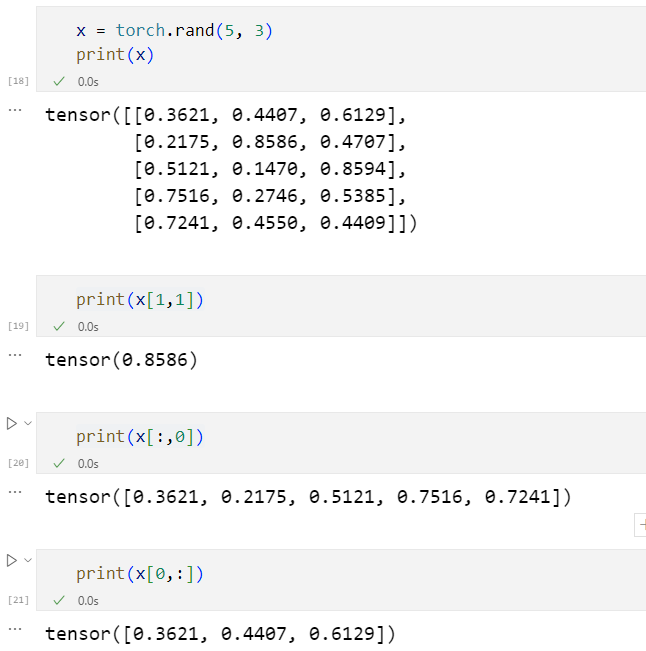
Numpy与Tensor的互转
python
a = torch.ones(5)
print(a)
b = a.numpy()
print(b)
print(type(b))
'''
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
print(a)
print(b)
'''
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
print(a)
print(b)
'''
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
print(a)
print(b)
'''