Vue3
简介
创建工程
目前是基于vite
目录结构,src,main.ts,index.HTML,App.vue
核心语法
OptionsAPI 与 CompositionAPI
OptionsAPI
vue2 使用,配置风格,分散,不利于维护
CompositionAPI
Vue3使用,组合风格,有序
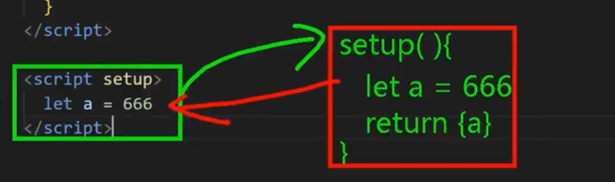
setup初识
没有this,this是undefined
setup的返回值可以是一个渲染函数
setup可以和OptionsAPI同时使用
setup是最早的生命周期,OptionsAPI可以读setup的,使用 this,但是 setup不能读取OptionsAPI的,没有this
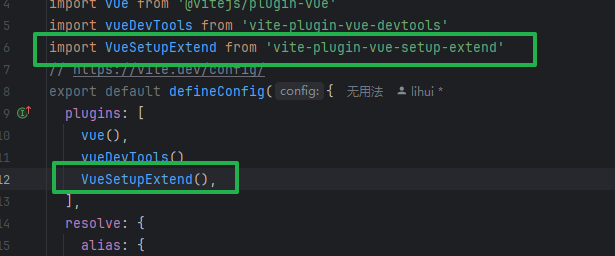
setup语法糖
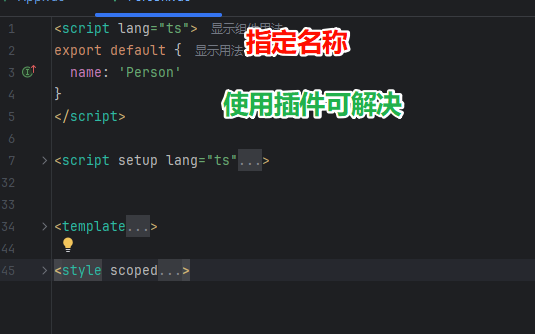
解决指定名称
一般工作中,不会用,因为一般名称与文件名是一样的
ref 基本响应式数据
方法中操作ref的 需要使用.value ,模版中不可以
ref 可以定义基本,可以定义对象
定于对象是操作数据需要用.value
ref 定义对象,底层使用reactive
<script lang="ts">
export default {
name: 'Person'
}
</script>
<script setup lang="ts">
//数据
import {ref} from "vue";
// 改用响应式数据
let name = ref("张三")
let age = ref(18)
let sex = "男"
// 不用改变,是不是响应式数据没关系
let tel = "123456789"
//方法
function showTel() {
alert(tel)
}
function changeName() {
name.value = "王五"
}
function changeAge() {
age.value++
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="person">
<h1>姓名:{{ name }}</h1>
<h2>年龄:{{ age }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<button @click="showTel">查看联系方式</button>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: #ddd;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
</style>reactive 对象类型响应数据
reactive 只能 定义对象的
reactive重新分配对象会失去响应式,可以使用(Object.assign去整体替换)
Object.assign(obj1,obj2,obj3), 2 给1,3 再给1
<script setup lang="ts">
// 数据
import {reactive} from "vue";
let car = reactive({brand: "保时捷", price: 1000})
// 方法
function changePrice() {
car.price += 10
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<div class="person">
<p>品牌:{{ car.brand }}</p>
<p>价格:{{ car.price }}</p>
<button @click="changePrice">修改价格</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: #ddd;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
</style>toRefs toRef
解构响应式对象里的内容,并且依然可以具备响应式的能力
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{ person.age }},{{ nl }}</h2>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {reactive, toRefs, toRef} from 'vue'
// 数据
let person = reactive({
name: '张三',
age: 18
})
// 使用toRefs从person这个响应式对象中,解构出name、age,且name和age依然是响应式的
// name和age的值是ref类型,其value值指向的是person.name和person.age
let {name, age} = toRefs(person)
let nl = toRef(person, 'age')
console.log(nl.value)
// 方法
function changeName() {
name.value += '~'
console.log(name.value, person.name)
}
function changeAge() {
age.value += 1
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: skyblue;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
li {
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>计算属性 computed
计算属性,算出来的也是响应数据
读写
let fullName = computed({
//读
get() {
return firstName.value.slice(0, 1).toUpperCase() + firstName.value.slice(1) + '-' + lastName.value
},
// 写
set(val) {
const [str1, str2] = val.split('-')
firstName.value = str1
lastName.value = str2
}
})watch
监视数据的变化(作用与vue2一样)
vue3的Watch只能监视以下四种数据
- ref定义的数据
- reactive 定义的数据
- 函数返回的一个值,即getter函数
- 一个包含上述内容的数组
watch(监视的,监听的回调)
第一种情况
情况一:监视【ref】定义的【基本类型】数据
<template>
<div class="person">
<h1>情况一:监视【ref】定义的【基本类型】数据</h1>
<h2>当前求和为: {{ sum }}</h2>
<button @click="changeSum">点我sum+1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {ref, warn, watch} from "vue";
// 数据
let sum = ref(0)
// 方法
function changeSum() {
sum.value++
}
// 计算属性
// 监听
// watch(监视的,监听的回调)
// 情况一:监视【ref】定义的【基本类型】数据
/*watch(sum, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log("变化了")
})*/
// 情况一:监视【ref】定义的【基本类型】数据
const stopWatch = watch(sum, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log("变化了")
if (newValue > 5){
stopWatch()
}
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: skyblue;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
li {
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>第二种情况
监视【ref】定义的【对象】数据,需要手动深度监视
若修改的是ref定义的对象中的属性,newValue和oldValue都是新值,因为它们是同一个对象。
若修改整个ref定义的对象,newValue是新值,oldValue是日值,因为不是同一个对象了。
监视的是对象的地址值,若想监视对象内部属性的变化,需要手动开启深度监视 watch的第一个参数是:被监视的数据 watch的第二个参数是:监视的回调 watch的第三个参数是:配置对象(deep、immediate等等.....)
第三种情况
监视【reactive 】定义的【对象】数据,默认是深度监听的
改变仍然是同一个对象
第四种情况
监视ref或reactive定义的【对象类型】数据中的某个属性
- 该属性不是对象类型,需要写成函数式的
- 该属性还是对象类型的,可以直接编,也能写函数,但是建议写成函数
第五种情况
监视上述的多个数据
watch([() => person.name, () => person.car], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('person.car变化了', newValue, oldValue)
}, {deep: true})监视上述四种的,多数据的
// 监视,情况五:监视上述的多个数据
watch([() => person.name, () => person.car], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('person.car变化了', newValue, oldValue)
}, {deep: true})WatchEffect
watchEffect:不用明确指出监视的数据(函数中用到哪些属性,那就监视哪些属性)
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>需求:当水温达到60度,或水位达到80cm时,给服务器发请求</h2>
<h2>当前水温:{{ temp }}℃</h2>
<h2>当前水位:{{ height }}cm</h2>
<button @click="changeTemp">水温+10</button>
<button @click="changeHeight">水位+10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref, watch, watchEffect } from 'vue'
// 数据
let temp = ref(10)
let height = ref(0)
// 方法
function changeTemp() {
temp.value += 10
}
function changeHeight() {
height.value += 10
}
// 监视 -- watchEffect实现
watchEffect(() => {
if (temp.value >= 60 || height.value >= 80) {
console.log('给服务器发请求')
}
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: skyblue;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
li {
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>标签ref
作用:用于注册模板引用。
用在普通
DOM标签上,获取的是DOM节点。用在组件标签上,获取的是组件实例对象。
props
// 只接收list
/*defineProps(['list'])*/
// 接收list + 保存props
/*let x = defineProps(['list'])
console.log(x)*/
// 接收list + 限制类型
/*defineProps<{list:Persons}>()*/
// 接收list +限制类型 + 默认值
withDefaults(defineProps<{list:Persons}>(),{
list:()=>[{
id:'1', name:'赵四', age:18
}]
})生命周期
创建、挂载、更新、销毁
vue2
vue生命周期分为四个阶段 第一阶段(创建阶段):beforeCreate,created
第二阶段(挂载阶段):beforeMount(render),mounted
第三阶段(更新阶段):beforeUpdate,updated
第四阶段(销毁阶段):beforeDestroy,destroyed
vue3
创建阶段:setup
挂载阶段:onBeforeMount onMounted
更新阶段:onBeforeUpdate onUpdated
卸载阶段:onBeforeUnmount onUnmounted
hooks
import useSum from "@/hooks/useSum.ts";
import useDog from "@/hooks/useDog.ts";
const {sum,add} = useSum()
const {dogList,getDog} = useDog()import {reactive, ref} from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
export default function () {
let sum = ref(0)
function add() {
sum.value++;
}
return {sum, add}
}路由
介绍
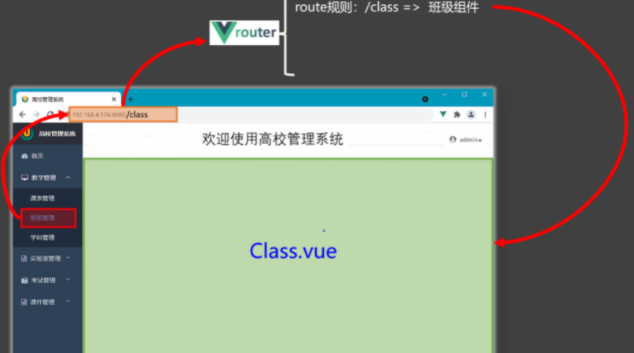
app.vue main.js 都要改
路由组件通常存放在
pages或views文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹。通过点击导航,视觉效果上“消失” 了的路由组件,默认是被卸载掉的,需要的时候再去挂载。
- 路由组件:靠路由规则渲染出来的。
route:[{path:/demo,component:demo}] - 一般组件:亲手写出来的标签。
<demo/>
路由器工作模式
history模式优点:
URL更加美观,不带有#,更接近传统的网站URL。缺点:后期项目上线,需要服务端配合处理路径问题,否则刷新会有
404错误。jsconst router = createRouter({ history:createWebHistory(), //history模式 /******/ })各版本:
vue2——
mode:'history'vue3——
history:createWebHistory()React——
BrowserRouterhash模式优点:兼容性更好,因为不需要服务器端处理路径。
缺点:
URL带有#不太美观,且在SEO优化方面相对较差。vueconst router = createRouter({ history:createWebHashHistory(), //hash模式 /******/ })to的两种写法
vue<!-- 第一种:to的字符串写法 --> <router-link active-class="active" to="/home">主页</router-link> <!-- 第二种:to的对象写法 --> <router-link active-class="active" :to="{path:'/home'}">Home</router-link>
命名路由
给路由规则命名
routes:[
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
name:'xinwen',
path:'/news',
component:News,
},
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:About
}
]参数传递
query参数
传递参数
vue<!-- 跳转并携带query参数(to的字符串写法) --> <RouterLink :to="`/news/detail?id=${news.id}&title=${news.title}&content=${news.content}`">{{news.title}}</RouterLink> <!-- 跳转并携带query参数(to的对象写法) --> <RouterLink :to="{ //name:'xiang', //用name也可以跳转 path:'/news/detail', query:{ id:news.id, title:news.title, content:news.content } }" > {{news.title}} </RouterLink>接收参数:
jsimport {useRoute} from 'vue-router' const route = useRoute() // 打印query参数 console.log(route.query)
params参数
传递参数
vue<!-- 跳转并携带params参数(to的字符串写法) --> <RouterLink :to="`/news/detail/001/新闻001/内容001`">{{news.title}}</RouterLink> <!-- 跳转并携带params参数(to的对象写法) --> <RouterLink :to="{ name:'xiang', //用name跳转 // 不能用 path params:{ id:news.id, title:news.title, content:news.title } }" > {{news.title}} </RouterLink>接收参数:
jsimport {useRoute} from 'vue-router' const route = useRoute() // 打印params参数 console.log(route.params)
传递
params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,必须使用name配置项,不能用path。传递
params参数时,需要提前在规则中占位。
路由的props配置
作用:让路由组件更方便的收到参数(可以将路由参数作为props传给组件)
{
name:'xiang',
path:'detail/:id/:title/:content',
component:Detail,
// props的对象写法,作用:把对象中的每一组key-value作为props传给Detail组件
// props:{a:1,b:2,c:3},
// props的布尔值写法,作用:把收到了每一组params参数,作为props传给Detail组件
// props:true
// props的函数写法,作用:把返回的对象中每一组key-value作为props传给Detail组件
props(route){
return route.query
}
}replace属性
replace - 覆盖
push - 压入(栈)追加
重定向
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/home'
}其他
v-on
监听事件
缩写是 @
v-for
let games = reactive(
[
{id:'aysdytfsatr01',name: "王者"},
{id:'aysdytfsatr02',name: "火影"},
{id:'aysdytfsatr03',name: "原神"},
])
<h1>游戏列表</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="game in games" :key="game.id">{{game.name}}</li>
</ul>v-bind
单项绑定,数据流向页面,一般绑定图片等
缩写是 :
v-model
双向绑定,一般用于输入
v-if
按条件渲染,切换时,区块监听器和组件都会被销毁 重建
v-show
无论如何,都会被渲染,只有CSS display会切换
v-if 有更高的切换开销,而 v-show 有更高的初始渲染开销。因此,如果需要频繁切换,则使用 v-show 较好;如果在运行时绑定条件很少改变,则 v-if 会更合适。
ts 接口泛型自定义类型
// 定义一个接口,用于限制person对象的具体属性
export interface PersonInter {
id:string,
name:string,
age:number
}
// 一个自定义类型
// export type Persons = Array<PersonInter>
export type Persons = PersonInter[]- [x] v-on 绑定事件 就是 @
- [x] v-show 全是渲染
- [x] v-if 条件渲染
- [x] v-bind 绑定 单项 :
- [x] v-model 双向绑定
- [x] computed 计算属性
- [x] watch 监视 5种
- [x] ref 响应式 可对象 可基本
- [x] reactive 只能对象